Execution Logic
Once launched, HybridPetya checks if the target system uses UEFI with GPT partitioning. If confirmed, it drops multiple files into the EFI partition, including:
\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\config(encryption keys and victim ID)\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\verify(decryption validation)\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\counter(encryption progress tracker)\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi.old(backup of original bootloader)\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\cloak.dat(XORed bootkit for bypass variant)
The ransomware replaces the original bootloader with the vulnerable reloader.efi and removes \EFI\Boot\bootx64.efi.
Execution logic
Source: ESET
Victims are then forced into a reboot, triggering encryption of MFT clusters using Salsa20, while a fake CHKDSK screen hides the process.
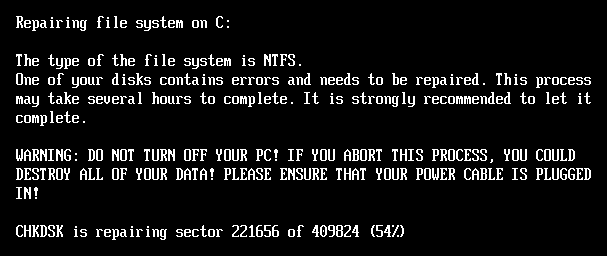 Fake CHKDSK message
Fake CHKDSK message
Source: ESET
Ransom Demand
After encryption completes, the system reboots again, and victims are shown a ransom note demanding $1,000 in Bitcoin.
The note offers a 32-character key that can be entered to:
- Restore the original bootloader
- Decrypt encrypted clusters
- Reboot the system back to normal operation
Unlike NotPetya, which offered no recovery, HybridPetya includes a functional decryption mechanism, suggesting it is financially motivated.
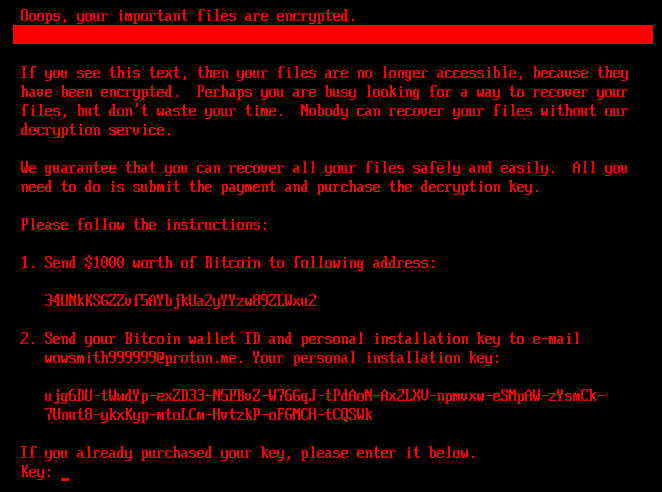 HybridPetya’s ransom note
HybridPetya’s ransom note
Source: ESET